Glossary
- Thread calculator:
- All calculated results are based on; Basic outside diameter, Pitch, Location and Pitch Tolerances as per "my" best interpretation of ASME B1.13M-2005.
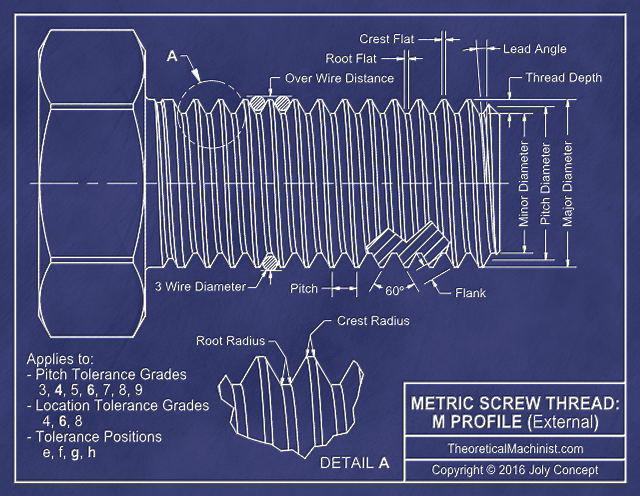
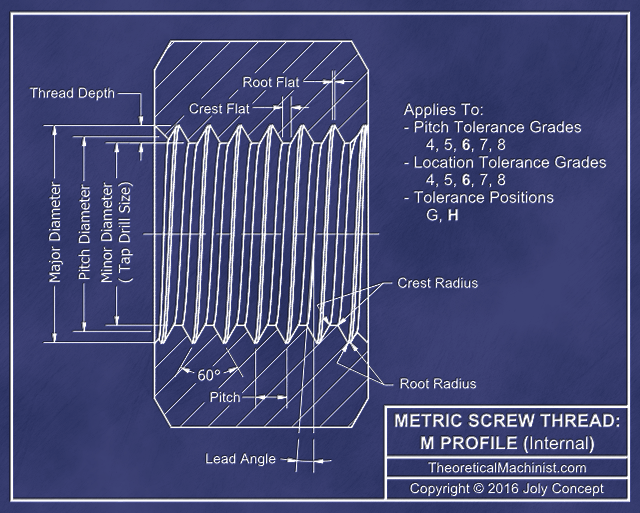
- M Profile: (ISO Metric Screw Thread form)
- A standard that describes the shape of an internal or external thread using metric millimeter dimensions. Making a thread that follow these specifications will ensure that it will work with threaded holes and shafts made by other manufacturers that follow these common specifications.
- NOTE: Metric threads and Imperial threads are not compatible and the use of both standards on a single component is discouraged.
- Basic diameter:
- This is the approximate largest diameter of the helical portion of a thread. The largest external diameter of a screw and the largest internal diameter of a threaded hole.
- NOTE: The size of the hexagon of a bolt or nut has no relevance when defining a thread size.
- Pitch:
- The distance between each "V"s after one 360-degree rotation along the helical portion of a screw shaft or hole.
- NOTE:The larger the size of a pitch dimension is, the larger the “V”s along the shaft or hole will be and vise versa.
- other NOTE: The larger the Pitch or size of the “V”s, the stronger a thread is considered. The greater width of the “V” shape augments the shearing strength of the thread. A smaller Pitch makes for a smoother running thread due to the smaller differences between the external and internal thread clearances.
-
- Tolerances: (Pitch and Location)
- Note: Selecting External or Internal thread: External threads are defined using lower case classes. Internal threads are define using Upper case classes.
-
- Pitch
- Pitch grade: The number, (grade), indicates the precision of the pitch diameter tolerance relative to the screw size and pitch combination; a smaller number indicated a tighter fit while a higher number means a looser fit. From 3 to 9 for external threads and from 4 to 8 for internal threads. If unsure of how to apply these parameters, 6 is the typical grade for both, internal and external threads
- Pitch class: Defined using a letter that is added or subtracted from the Pitch grade that affect the positional relationship between the external and external Pitch diameters of the screw and threaded hole.
- NOTE: Think of it as how much they are allowed to move from side to side within each other at the pitch diameter.
-
- Location
- Location grade: The number, (grade), indicate the precision of the major and minor diameter tolerance relative to the screw size and pitch combination; a smaller number indicated a tighter fit while a higher number means a looser fit. 4, 6, 8 for external threads. 4 to 8 for internal threads. If unsure of how to apply these parameters, 6 is the typical grade for both, internal and external threads
- Location class: Defined using a letter, (class), that is added or subtracted from the Location grade; e, f, g, h for external threads, G, H for internal threads. g/G are the common selections.
- NOTE: Think of it as the positional relationship between two parts bolted together. The screw going through a hole or a shaft going through a threaded hole. The movement allowed from side to side between both components.
-
- General usage:
- Normal tolerance: 6g (6g6g)
- Tighter tolerance: 4g6g
- No allowance: 6h (6h6h), 6H (6H6H)
- no. (of) Starts:
- This is the quantity of helical entries along the length of the screws. Typical screws have only one. Thread with multiple starts advance a greater distance for each turn.
- Example: A screw with one start and a pitch of 1.75mm will advance 1.75mm per 360 turn. A thread with a pitch of 1.5mm with 2 starts will advance 1.5mm x 2 = 3.0mm per 360 turn.
- Engagement (length):
- Adjusts the Pitch Tolerance as per the length of threads that will be physically engaged. Short (S) engagement will make the pitch diameter a tighter fit while a long (L) engagement will make the pitch diameter a looser fit.
- Direction: RH (Right Hand), LH (Left Hand)
- Right-handed threads tighten when rotating it clockwise. Left-handed threads tighten when rotating it counter clockwise. This parameter does not affect the dimension of the thread. Common threads are (RH) Right-handed.
- Root Radius:
- This parameter is for manufacturing convenience only. It affects the data generated for: radius depth, radius flank depth, flat depth and flat flank depth. If a radius of flat width is entered that is too large to manufacture a functional thread. The input will revert back to the default values.
- This parameter does not affect the dimensions generated for: Major diameter, Pitch diameter and Minor diameter.
Last Updated: 25 June 2025